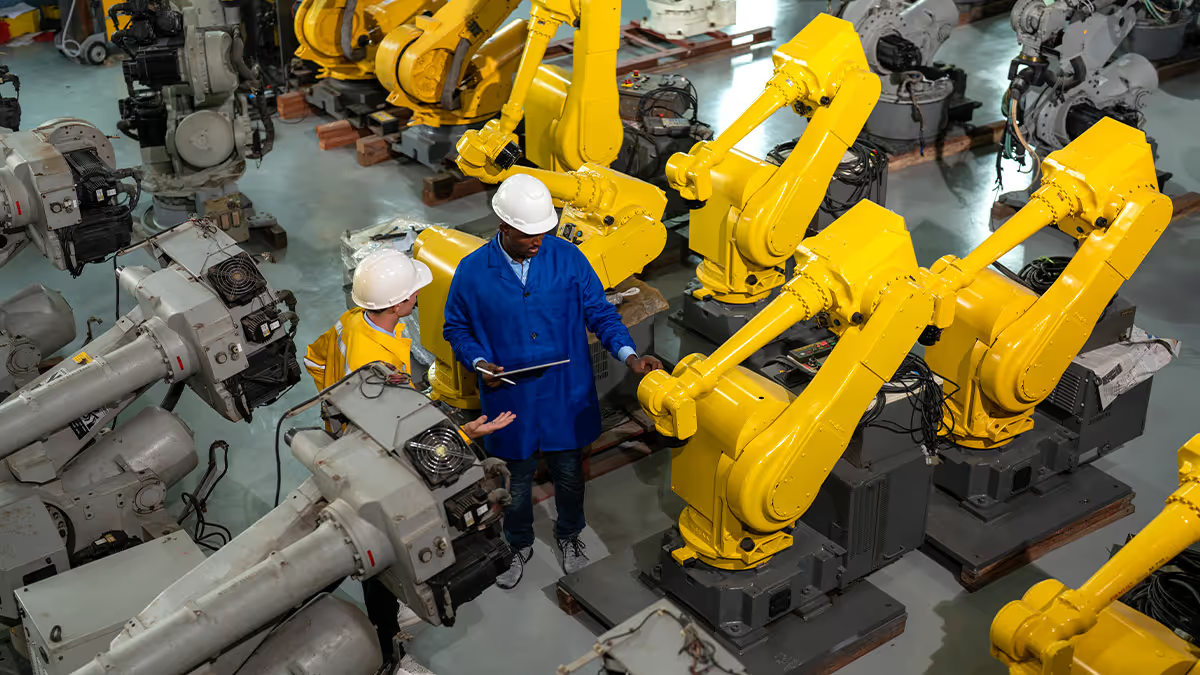
Bengaluru, often dubbed India’s Silicon Valley, is fast becoming a nucleus for logistics innovation. With the exponential rise in e-commerce and retail, warehouse operations are feeling the pressure to deliver faster, cheaper, and more efficiently. Enter warehouse robotics powered by reinforcement learning (RL), a cutting-edge approach that’s transforming how warehouses operate.
This article explores how reinforcement learning is revolutionising warehouse robotics, particularly in Bengaluru’s logistics sector. If you are enrolled in a data science course in Bangalore, understanding RL applications in warehousing can give you a competitive edge in capstone projects and future job roles.
Why Reinforcement Learning is Ideal for Warehouse Robotics
Reinforcement learning, a specific branch of machine learning, is all about training agents (like robots) to make sequences of decisions by rewarding good behaviour and penalising poor ones. In the complex environment of a warehouse, where robots must navigate aisles, pick items, and avoid obstacles, RL provides the flexibility and adaptability that rule-based systems lack.
Traditional automation relies heavily on pre-programmed routes and simple decision trees. But modern warehouses require dynamic solutions where robots can adapt to:
- Changing inventory layouts
- Sudden obstacles
- Variations in demand and order priority
- Multi-agent coordination between several robots
With reinforcement learning, warehouse robots can learn from their environment, optimising their picking routes, improving energy efficiency, and reducing operation time with each iteration. This is especially important as the size and complexity of warehouse spaces in Bengaluru continue to grow.
Key Components of an RL-Powered Warehouse System
For students pursuing a course, it’s important to grasp the core technologies involved:
- Robotic Hardware: Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are commonly used.
- Sensors and Cameras: To actively perceive the environment and avoid collisions.
- Reinforcement Learning Algorithms: Such as Q-Learning, Deep Q Networks (DQN), and Proximal Policy Optimisation (PPO).
- Simulators: Tools like Gazebo or Unity ML-Agents help train models virtually before deploying in the real world.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Integrate the RL models with broader inventory and order management.
Beyond these components, cloud computing and edge AI also play vital roles in processing data from hundreds of sensors and feeding actionable intelligence back to the robots in real time.
Benefits of RL in Bengaluru’s Logistics Ecosystem
Bengaluru’s logistics sector is unique due to high demand from tech firms, e-commerce giants, and third-party logistics providers. Applying reinforcement learning offers multiple benefits:
- Operational Efficiency: Robots learn to find the shortest and safest paths in real-time.
- Cost Reduction: Minimises energy consumption and reduces wear and tear.
- Scalability: RL models can handle more robots and larger warehouses without reprogramming.
- Faster Fulfilment: Reduces order-to-dispatch time, which is crucial in competitive markets like Bengaluru.
- Reduced Human Error: Automated systems make fewer mistakes compared to manual operations.
Furthermore, RL helps businesses adapt quickly to seasonal peaks and unforeseen disruptions, giving Bengaluru’s warehouses a much-needed competitive advantage.
Innovative Capstone Project Ideas
If you’re enrolled in a course, here are some capstone project ideas that leverage RL for warehouse automation:
1. Dynamic Path Optimisation for Multiple Robots
Use multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) to optimise navigation for several robots working simultaneously, avoiding collisions and bottlenecks.
2. Adaptive Inventory Repositioning
Develop an RL model that learns which high-demand items should be placed closer to dispatch areas based on changing order patterns.
3. Energy-Efficient Task Allocation
Create a system where RL agents decide which robot should handle which task, minimising overall energy consumption.
4. Human-Robot Interaction Models
Design models that enable robots to adapt their routes and speeds in environments where human workers are present, ensuring safety and efficiency.
5. Reinforcement Learning for Sorting Systems
Apply RL to conveyor-based sorting systems to dynamically adjust routes and sorting priorities based on incoming parcel loads.
Real-World Applications in Bengaluru
Several logistics companies and startups in Bengaluru are already experimenting with warehouse automation and robotics:
- E-commerce giants like Flipkart and Amazon have heavily invested in robotic fulfilment centres.
- Startups such as GreyOrange and Addverb Technologies are developing warehouse robotics solutions powered by AI and RL.
- Third-party logistics providers are adopting smarter systems to remain competitive.
For students working on projects or internships, collaborating with these companies offers valuable real-world exposure. Bengaluru’s thriving startup ecosystem also opens doors for entrepreneurial ventures focused on warehouse automation.
Skills Gained Through RL Projects
Engaging in reinforcement learning projects allows you to build a versatile skill set:
- Understanding of RL algorithms and environments
- Proficiency in Python and ML libraries (TensorFlow, PyTorch)
- Simulation environment handling (e.g., OpenAI Gym)
- Data preprocessing and reward engineering
- Integration of models with hardware systems
- Cloud deployment and monitoring
These skills are not only applicable to warehousing but also extend to other sectors like autonomous vehicles, gaming AI, financial modelling, and healthcare robotics.
Additional Project Expansion Ideas
To take your capstone to the next level, consider:
- Hybrid Models: Combine RL with supervised learning for initial training.
- Digital Twin Integration: Sync real-world warehouses with virtual simulations.
- Explainability: Build dashboards that explain robot decisions to human operators.
- Multi-Agent Coordination: Develop complex scenarios where multiple RL agents cooperate or compete to achieve warehouse goals.
Such enhancements will make your project robust and appealing to potential employers. Adding real-world metrics like task completion time, energy usage, and error rates can also make your solution measurable and impactful.
Future Trends in RL and Warehouse Robotics
The field of warehouse robotics is evolving rapidly, and RL is set to play an even bigger role. Emerging trends include:
- Edge AI: Running RL models directly on robots for real-time decision-making.
- Federated Learning: Allowing robots across different warehouses to learn collaboratively without sharing sensitive data.
- Sustainable Warehousing: Using RL to optimise energy usage and reduce carbon footprints.
- 5G Connectivity: Enabling ultra-low latency communication between RL models and robotic systems.
Conclusion: Bengaluru’s Logistics Future is AI-Driven
As Bengaluru continues its trajectory as an innovation hub, the logistics sector stands on the brink of an AI-driven transformation. Reinforcement learning offers the perfect blend of adaptability and optimisation needed for warehouse robotics in this dynamic environment.
By undertaking projects in this area as part of your data science course, you not only gain practical skills but also contribute to shaping the future of logistics in one of India’s most vibrant tech ecosystems.
So, whether you’re a student or a budding data scientist, diving into RL-powered warehouse automation could be your gateway to impactful innovations in Bengaluru’s booming logistics industry. Embrace this exciting field, and you could be at the forefront of the next wave of supply chain evolution.
ExcelR – Data Science, Data Analytics Course Training in Bangalore
Address: 49, 1st Cross, 27th Main, behind Tata Motors, 1st Stage, BTM Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560068
Phone: 096321 56744